
Project Update
SoCalGas values its relationship with UC Irvine and its role in the Irvine community. As we continue striving to deliver natural gas in a safe, reliable, and affordable manner, we remain committed to transparency with the community regarding our proposed hydrogen blending demonstration project.
On July 1, 2025, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) held two public participation hearings (PPHs) at 2:00 pm and 6:00 pm at University High School in Irvine. The PPHs were scheduled by the CPUC in May 2025 in connection with the Joint Amended Application filed by SoCalGas, SDG&E, PG&E, and Southwest Gas proposing hydrogen blending demonstration projects, as directed by the CPUC. These hearings allow the public to learn about the projects, share opinions, and communicate directly with the CPUC.
We want to extend our sincere thanks to everyone who attended the July 1st PPHs and shared their valuable feedback. We continue to encourage the community to remain engaged and informed about the proposed demonstration project. For more information, please visit the CPUC’s website.
At the direction of the California Public Utilities Commission, SoCalGas is proposing a local demonstration project that could safely blend up to 20% clean renewable hydrogen into the natural gas system in an isolated portion of the University of California, Irvine (UCI) campus.
To support California’s climate and clean air goals, SoCalGas is proposing a hydrogen blending demonstration project at the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Anteater Recreation Center. This project will blend clean renewable hydrogen into a portion of UCI’s natural gas system and offer a real-world environment to better understand how clean renewable hydrogen and natural gas can be safely delivered to customers in the future. This is part of a broader effort by California and utilities to develop a standard for safe hydrogen blending, which could reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. The data gathered from this demonstration can also help assess how to speed the development and deployment of related advanced technologies key to the state’s climate and clean air goals.
Project Overview:
- Project will begin demonstrating a 5% blend, gradually increasing up to 20% into SoCalGas’s infrastructure that will serve the Anteater Recreation Center (ARC) at UCI.
- The hydrogen blend will be used for light commercial equipment.
- Active blending expected to last approximately 18 months on the campus.
How Hydrogen Blending Would Work at UCI
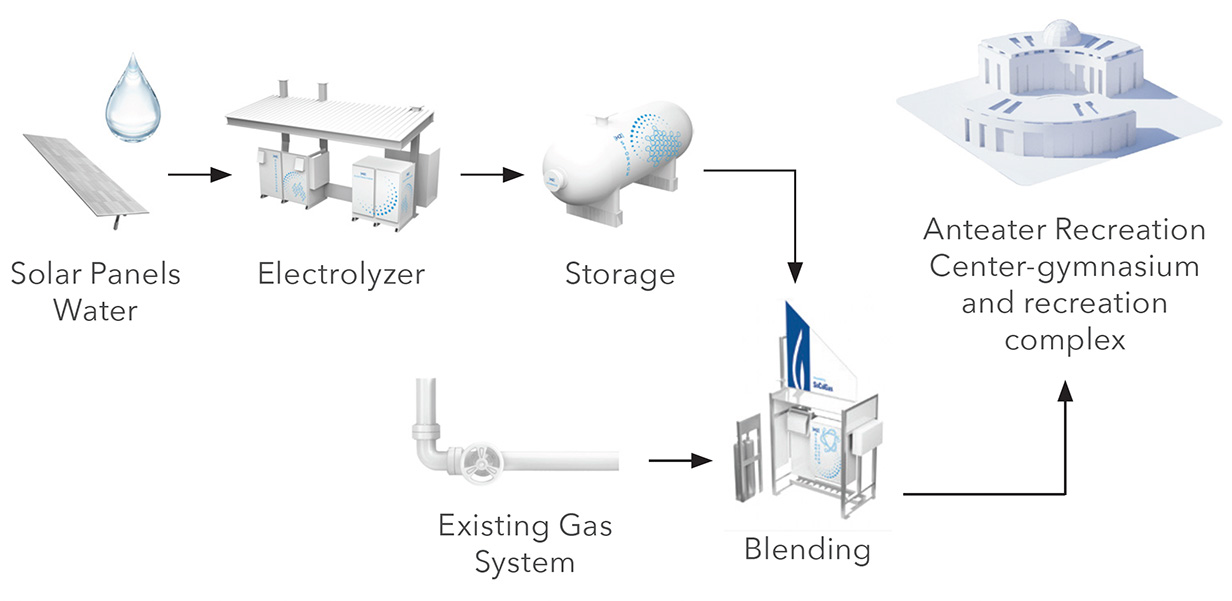
Hydrogen and General Safety Overview
Blended hydrogen is a fuel that has been safely and reliably utilized around the world for decades. For example, Hawaiʻi Gas has been using hydrogen in its fuel mix for a half-century and has more than 1,100 miles of pipelines that transport up to 15% hydrogen, serving homes, schools, restaurants, and businesses. Here’s what our research found:
• Hydrogen is no more or less dangerous than other flammable fuels, including gasoline and natural gas. In fact, some of hydrogen’s differences actually provide safety benefits compared to gasoline or other fuels.1
• If a pipeline is leak-tight for natural gas, it would also be leak-tight for a hydrogen blend.2
• Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and is both non-toxic and non-poisonous.3
• Hydrogen is lighter than air and diffuses rapidly.4
• The US currently produces about 10 million metric tons of hydrogen each year.5
• For decades, hydrogen has been safely used in the chemical and refining industries.6
• Hydrogen has been blended into existing gas infrastructure to help decarbonization efforts by a variety of localities around the world for decades:
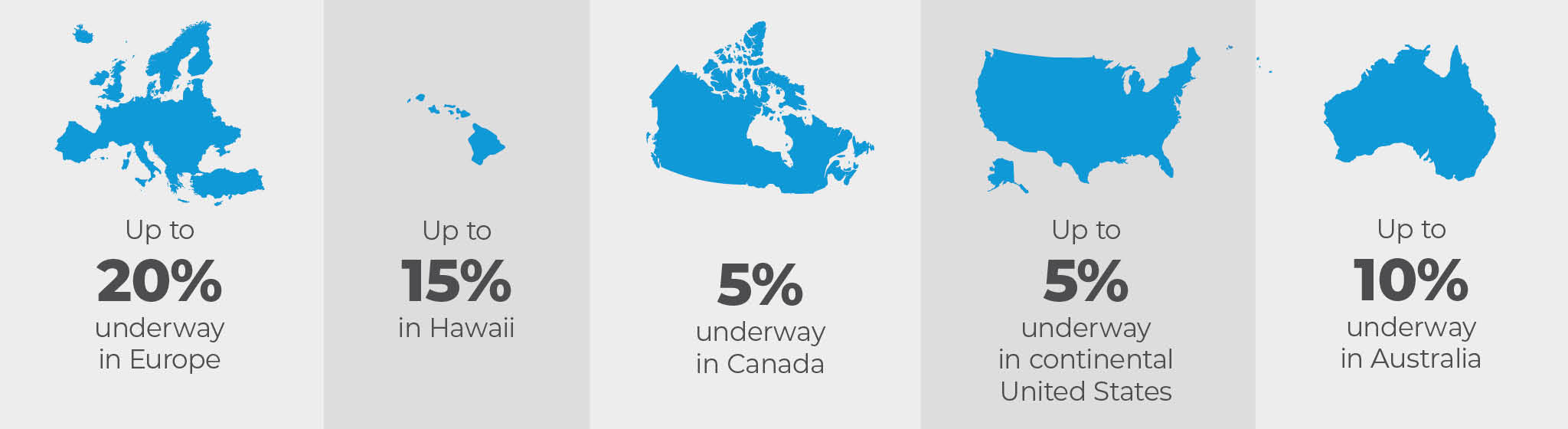
The above showcases hydrogen blended at various percentages by volume
SoCalGas Has a Robust Safety Plan for UC Irvine
We understand that those working and residing near the demonstration project locations may have concerns. Here’s how we plan to help address those concerns:
• Install remote methane/hydrogen monitoring systems that are active 24/7 and monitored in real-time.
• Perform leak surveys before, after, and on a monthly basis during implementation.
• Survey end-use customer equipment monthly to confirm behind-the-meter equipment is operating safely.
• Conduct gas system operational tests monthly and production site equipment tests on a monthly, quarterly, and yearly frequency based on manufacturer recommendations.
• Provide hydrogen safety education for school and emergency personnel.
• Create specific hydrogen blending customer protocols and emergency response plans.
Benefits of Hydrogen Blending
Hydrogen blending has the potential to expedite the transition to a net-zero energy future by:
- Leveraging the state's current infrastructure, skilled workforce, and regulatory framework to deliver cleaner fuel to customers
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions on both the electric and gas grids
- Serving as a low-cost hydrogen storage and transportation medium
- Providing system resiliency through energy diversity and redundancy
- Allowing Californians to continue using existing appliances without modifications
A 20% clean renewable hydrogen blend in a natural gas system as large as California's could reduce carbon emissions equal to taking more than a million passenger vehicles off the streets annually.
Additional Resources
Hydrogen Blending Overview
UCI H2 Blending Fact Sheet
UCI Safety Fact Sheet
UCI Hydrogen Blending Map
UC Irvine Blending Demonstration Website
加州大學爾灣分校氫氣混合說明書
加州大學爾灣分校安全事實說明書
加州大學爾灣分校氫氣混合圖
For more information, contact us at ProjectInfo@socalgas.com or 844-765-9385
1. Source: U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). Hydrogen Safety Fact Sheet [Fact Sheet]. https://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/pdfs/h2_safety_fsheet.pdf
2. Source: GTI Energy. Climate Impacts of Fugitive Hydrogen Emissions. Center for Methane Research. https://www.gti.energy/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/CMR-Climate-Impacts-of-H2-Emissions.pdf
3. Source: U.S. DOE. Safety, Codes and Standards [Fact Sheet]. Fuel Cell Technologies Office. https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/articles/safety-codes-and-standards-fact-sheet
4. Source: U.S. DOE. Hydrogen Safety Fact Sheet [Fact Sheet]. https://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/pdfs/h2_safety_fsheet.pdf
5. Source: U.S. DOE Hydrogen Production Website. https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-production
6. Source: WHA International, Inc Website. Top Industrial Uses of Hydrogen, and the Need for Industrial Hydrogen Safety. https://wha-international.com/hydrogen-in-industry/
Message funded by shareholders